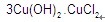Tel:0086-21-58356513, 58356613
Email:info@skybluechem.com
Site:www.skybluechem.com/
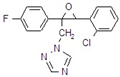
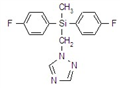
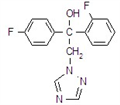
kasugamycin
Common name kasugamycin (JMAF)
CAS RN [6980-18-3]
kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate
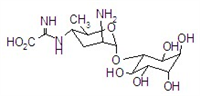
IUPAC name 1L-1,3,4/2,5,6-1-deoxy-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-4-(a-iminoglycino)-a-D-arabino-hexopyranoside hydrochloride hydrate; [5-amino-2-methyl-6-(2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyloxy)tetrahydropyran-3-yl]amino-a-iminoacetic acid hydrochloride hydrate
Chemical Abstracts name 3-O-[2-amino-4-[(carboxyiminomethyl)amino]-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-a-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl]-D-chiro-inositol hydrochloride hydrate
CAS RN [19408-46-9]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
kasugamycin
Mol. wt. 379.4 M.f. C14H25N3O9 pKa pKa1 3.23, pKa2 7.73, pKa3 11.0
kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate
Mol. wt. 433.8 M.f. C14H28ClN3O10 Form Colourless needle crystals. M.p. 202-204 ºC (decomp.) V.p. <1.3 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP <1 Henry <4.51 ´ 10-11 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 0.43 g/cm3 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 125 g/l (25 ºC). In methanol 2.76, acetone, xylene <1 (all in mg/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Very stable at room temperature. Stable in weak acids, but unstable in strong acids and alkalis. DT50 (50 ºC) 47 d (pH 5), 14 d (pH 9). Specific rotation [a]D25 +120?(c 1.6 H2O)
APPLICATIONS
kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate
Biochemistry Protein synthesis inhibitor. Inhibits binding of Met-RNA to the mRNA-30S complex, thereby preventing amino acid incorporation.
Mode of action Systemic fungicide and bactericide with protective and curative action. Inhibits hyphal growth of Pyricularia oryzae on rice, preventing lesion development; comparatively weak inhibitory action to spore germination, appressoria formation on the plant surface or penetration into the epidermal cell. Rapidly taken up into plant tissue and translocated. In contrast, against Cladosporium fulvum on tomatoes, inhibition of sporulation is strong, but inhibition of hyphal growth is weak.
Uses Control of fungal and bacterial diseases affecting rice, vegetables and fruit. On rice, it controls diseases caused by Pyricularia oryzae and Pseudomonas glumae (bacterial grain rot), with ground and aerial applications, at 20-30 g/ha, and seedling diseases caused by various bacterial pathogens, at 0.3-0.6 g/box. In sugar beet, it controls Cercospora beticola, at 80-100 g/ha. Also used to control plant diseases in various crops: Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans in cucumbers, at 30-60 g/ha; Colletotrichum lagenarium in melons and water melons; Cladosporium fulvum and Corynebacterium michiganense in tomatoes, at 20-40 g/ha; Mycovellosiella spp. in aubergines; Cercospora spp. in celery; Erwinia carotovora in potatoes, carrots and onions; Pseudomonas spp. (halo blight) in kidney beans, at 40-60 g/ha; Xanthomonas spp. in paprika; Venturia sp. in apples; Pseudomonas spp. in kiwifruit; etc.
Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to rice, tomatoes, sugar beet, potatoes and other vegetables, but slight injury has been noted to peas, beans, soya beans, grapes, citrus, and apples.